CodeQL 踩坑指南 - Java
讲解这东西的大师傅们太多了,不班门弄斧了,这里仅针对一些踩过的坑点提供一些自己的解决方案,希望能对一些师傅提供点帮助。
坑I - Lombok
场景
在构建一些小型cms和自己的一些项目时,突然发现构建好的数据库内源码比实际的源码少了一大半,导致很多规则分析的flow直接断掉了,什么规则扫描结果都没有。
原因
构建好的数据库文件夹下,源码是存放在src.zip下的。通过vscode的插件,将数据库添加后也可以看到构建加载后的源码。通过对比源码,发现丢失的java文件都存在lombok注解(@Data/@Sl4j)。
这里的原因就是由于项目使用了lombok。根据官方Github Issue 可得知,lombok 代码在编译期间使用注释处理器转换为正确的 Java 代码。这会干扰 CodeQL 分析器,该分析器会在源代码转换为有效的 Java 代码之前“查看”源代码,从而导致它跳过此类文件。
解决方案
按照官方的思路,解决方式就是将所有文件还原为不使用lombok的方式。还原的方案主要有两种:
1.通过Lombok.jar 直接还原文件
在官方的Github Issue 提供了一种方式。
下载项目对应版本的lombok.jar(或者从External Libraries寻找下载好的依赖jar包),运行:
java -jar lombok.jar delombok . -d "delombok-code"
但是在实际测试中,这种方式不会对项目内关联的代码进行还原,比如自己定义的一些TO类,在这种方式的还原下只会被还原成Object,而不是实际的TO对象。可能会对代码分析造成一定的影响。
2. 使用maven-delombok
在pom文件内增加:
<build > <plugins > <plugin > <groupId > org.projectlombok</groupId > <artifactId > lombok-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 1.18.4.0</version > <executions > <execution > <phase > generate-sources</phase > <goals > <goal > delombok</goal > </goals > <configuration > <encoding > UTF-8</encoding > <addOutputDirectory > false</addOutputDirectory > <sourceDirectory > src/main/java</sourceDirectory > <outputDirectory > ${project.basedir}/src/main/lombok</outputDirectory > </configuration > </execution > </executions > </plugin > </plugins > </build >
由于将所有的还原lombok指向目录/src/main/lombok,所以在maven编译的时候,我们希望编译的是lombok还原后的目录,这样codeql才能够读取整个有效的过程,所以需要修改sourceDirectory
<build > <sourceDirectory > ${project.basedir}/src/main/lombok </sourceDirectory > ...... </build >
这里提供一个脚本, 快速插入lombok-plugins,将脚本放置项目根目录并运行python3 delombok.py ./pom.xml 即可。
import osimport reimport subprocessimport xml.etree.ElementTree as ETimport sysdef delbankline (file ): with open (file, 'r' ) as f: lines = [x for x in f.readlines() if not re.search(r'^\s+$' , x)] with open (file, 'w' ) as fw: fw.writelines(lines) def delombok (file ): with open (file, 'r+' ) as f: lines = f.readlines() f.seek(0 ) f.truncate() for line in lines: line = line.replace("<directory>${project.basedir}/src/main</directory>" , "<directory>${project.basedir}/src/main/lombok</directory>" ) line = line.replace('src/main/java' , 'src/main/lombok' ) f.write(line) tree = ET.ElementTree() XML_NS_NAME = "" XML_NS_VALUE = "http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" ET.register_namespace(XML_NS_NAME, XML_NS_VALUE) tree.parse(file) root = tree.getroot() pre = (re.split('project' , root.tag))[0 ] sourceDirectory = ET.Element("sourceDirectory" ) goal = ET.Element("goal" ) phase = ET.Element("phase" ) groupId = ET.Element("groupId" ) artifactId = ET.Element("artifactId" ) version = ET.Element("version" ) sourceDirectory.text = "${project.basedir}/src/main/lombok" goal.text = "delombok" phase.text = "generate-sources" groupId.text = "org.projectlombok" artifactId.text = "lombok-maven-plugin" version.text = "1.18.4.0" goals = ET.Element("goals" ) goals.append(goal) addOutputDirectory = ET.Element("addOutputDirectory" ) addOutputDirectory.text = "false" sourceDirectory2 = ET.Element("sourceDirectory" ) sourceDirectory2.text = "src/main/java" outputDirectory = ET.Element("outputDirectory" ) outputDirectory.text = "${project.basedir}/src/main/lombok" encoding = ET.Element("encoding" ) encoding.text = "UTF-8" configuration = ET.Element("configuration" ) configuration.append(encoding) configuration.append(addOutputDirectory) configuration.append(sourceDirectory2) configuration.append(outputDirectory) execution = ET.Element("execution" ) execution.append(phase) execution.append(goals) execution.append(configuration) executions = ET.Element("executions" ) executions.append(execution) plugin = ET.Element("plugin" ) plugin.append(groupId) plugin.append(artifactId) plugin.append(version) plugin.append(executions) build = root.find(pre + "build" ) if build is None : build = ET.Element("build" ) root.append(build) build.insert(0 , sourceDirectory) plugins = build.find(pre + "plugins" ) if plugins is None : plugins = ET.Element("plugins" ) build.insert(0 , plugins) plugins.insert(0 , plugin) tree.write(file, encoding="utf-8" , xml_declaration=True ) def relombok (file ): tree = ET.ElementTree() XML_NS_NAME = "" XML_NS_VALUE = "http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" ET.register_namespace(XML_NS_NAME, XML_NS_VALUE) tree.parse(file) root = tree.getroot() pre = (re.split('project' , root.tag))[0 ] build = root.find(pre + "build" ) if build is None : return plugins = build.find(pre + "plugins" ) if plugins is None or len (plugins)==0 : return for plugin in plugins: for child in plugin: if child.text == "lombok-maven-plugin" : plugins.remove(plugin) tree.write(file, encoding="utf-8" , xml_declaration=True ) if __name__ == "__main__" : file = sys.argv[1 ] delbankline(file) relombok(file) delombok(file) print ("finish!!" )
坑II - 扩展文件
场景
在看官方提供的ql规则时候,有一个特殊的规则引起了注意:MyBatisMapperXmlSqlInjection.ql
他做的事情是扫描Mapper配置Mybatis XML的${}的SQL注入,但是在我们的源代码中,完全没有看到相关的Mybatis的Mapper XML文件。所以规则扫描一直无效。
原因
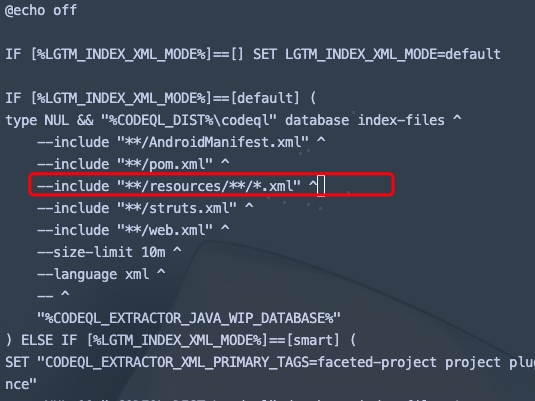
原因归结于我们没有把对应的xml文件加入到我们的数据库中,在默认的配置中,codeql仅加载了四种xml文件,分别为:
AndroidManifest.xml pom.xml struts.xml web.xml
解决方案
结局方案主要有两种方式。1.拆分codeql database create
codeql database init --source-root <YourSourcePath> --language java <YourDBPath> codeql database trace-command --working-dir=<YourSourcePath> <YourDBPath> <BuildCommand> codeql database index-files --language properties --include-extension .properties --working-dir=<YourSourcePath> --exclude=target <YourDBPath> codeql database index-files --language xml --include-extension .xml --working-dir=<YourSourcePath> --exclude=target <YourDBPath> codeql database finalize <YourDBPath>
2.修改pre-finalize 楼兰师傅的文章 学到了一种新的方式。
这种方法只提供xml文件的扩展,如果需要扩展其他类型文件,还需要自己手动增加。(因为 --language 参数不同)
windows: --include "**/resources/**/*.xml" ^
linux: --include "**/resources/**/*.xml"
加入properties扩展: if [ "${LGTM_INDEX_PROPERTIES_FILES:-false}" == "true" ]
注意,这种方法都加入了size-limit的限制,.xml默认限制10MB,.properties默认限制5MB。
坑III - 分析缓慢
场景
在一些巨型项目中,一次构建+分析可能需要花费10-15分钟,如果在构建的过程中发现忘记加载某些文件,这个过程就要再来一次,重复几次,一天的时间就无了。
原因
大型的项目构建速度缓慢,规则分析也很缓慢。
解决方案
使用mvnd 来代替mvn提速 mvn clean package -f "pom.xml" -B -V -e -Dfindbugs.skip -Dcheckstyle.skip -Dpmd.skip=true -Denforcer.skip -Dmaven.javadoc.skip -DskipTests -Dmaven.test.skip.exec -Dlicense.skip=true -Drat.skip=true
首先下载并安装mvnd , 官方的手册已经比较清晰。
然后修改codeql构建命令,并使用mvnd进行构建codeql database create codeqlDB --language=java --command="mvnd clean package -f "pom.xml" -B -V -e -Dfindbugs.skip -Dcheckstyle.skip -Dpmd.skip=true -Denforcer.skip -Dmaven.javadoc.skip -DskipTests -Dmaven.test.skip.exec -Dlicense.skip=true -Drat.skip=true
如果mvnd没有配置的话,还需要使用-s settings.xml指定mvn的setting配置文件。
大概优化的时间在20-30s左右,不同的项目优化效果不同。
规则分析参数调优 codeql query compile --warnings=hide --fast-compilation --dump-qlo
优化I - python库
场景
在经历上述坑点之后,我的数据库构建已经成为了一个很复杂的过程。经常需要各种脚本来辅助。脚本的代码就会出现很丑陋的:os.system("codeql database xxxxxx ......"), 令人难以忍受。
解决方案
偶然在Github发现了一个非官方的python-codeql库 , 封装了大量常用的codeql操作。pip3 install git+https://github.com/AlexAltea/codeql-python.git
import codeqldb = codeql.Database('path/to/db.zip' ) results = db.query('select "Hello"' ) assert (results[0 ][1 ] == 'Hello' )codeql.set_search_path('path/to/codeql' ) results = db.query(''' import cpp from BlockStmt block select block ''' )db = codeql.Database.from_cpp(''' int main() { return 1337 + 1337 + 1337; } ''' )results = db.query(''' import cpp from Literal literal where literal.getType() instanceof IntType and literal.getValue().toInt() = 1337 select literal ''' )assert (len (results[1 :]) == 3 )
优化II - 部分规则Demo
有了坑II的支持,现在已经可以扫描如spring boot内的配置文件了。例如H2-Console的JNDI注入。
在这个规则中,检测了两个事情:
是否存在com.h2database.h2这个jar.
是否开启了spring.h2.console.enabled
import java import semmle.code.configfiles.ConfigFiles import semmle.code.xml.MavenPom private class H2databaseDependency extends Dependency { H2databaseDependency() { this.getAChild("groupId").getTextValue() = "com.h2database" and this.getAChild("artifactId").getTextValue() = "h2" } } class ApplicationProperties extends ConfigPair { ApplicationProperties() { this.getFile().getBaseName() = "application.properties" } } from H2databaseDependency dependency, ApplicationProperties apwhere ap.getFile() .getParentContainer() .getAbsolutePath() .matches (dependency.getFile().getParentContainer().getAbsolutePath() + "%") and exists ( | ap.getNameElement().getName() = "spring.h2.console.enabled" and ap.getValueElement().getValue() = "true" ) and not ap.getFile().getAbsolutePath().matches ("%test/resources%") select ap, "该配置存在H2 Database JNDI注入漏洞"
这里只是抛砖引玉,有了配置文件,可以快速的对比SCA,来检查是否使用了存在漏洞的三方jar包。
结尾
暂时想到的就这些,还有一些从网络上学到的一些小东西就不丢人现眼了...如果有错误或其他的一些小tips,恳求各位师傅指点一二🙇。
参考链接
1.Github Issue : https://github.com/github/codeql/issues/8363 https://github.com/github/codeql/issues/4984#:~:text=Unfortunately Lombok does not work with the CodeQL,the source files before running CodeQL as follows%3A https://github.com/github/codeql/blob/main/java/ql/src/experimental/Security/CWE/CWE-089/MyBatisMapperXmlSqlInjection.ql https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/egjA2xFm_ziGHjJ7IxOCbg https://github.com/apache/maven-mvnd https://github.com/AlexAltea/codeql-python